What Are Homogenizer Beads and How Do They Work in Sample Preparation?
22nd Oct 2025
Homogenizer beads are essential tools in laboratories for breaking down complex biological samples quickly and efficiently. By using rapid agitation, these small particles disrupt cell walls and tissues, making it easier to extract valuable biomolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. Let’s explore what homogenizer beads are, how they work, and how to choose the right ones for your laboratory needs.
What Are Homogenizer Beads Made Of?
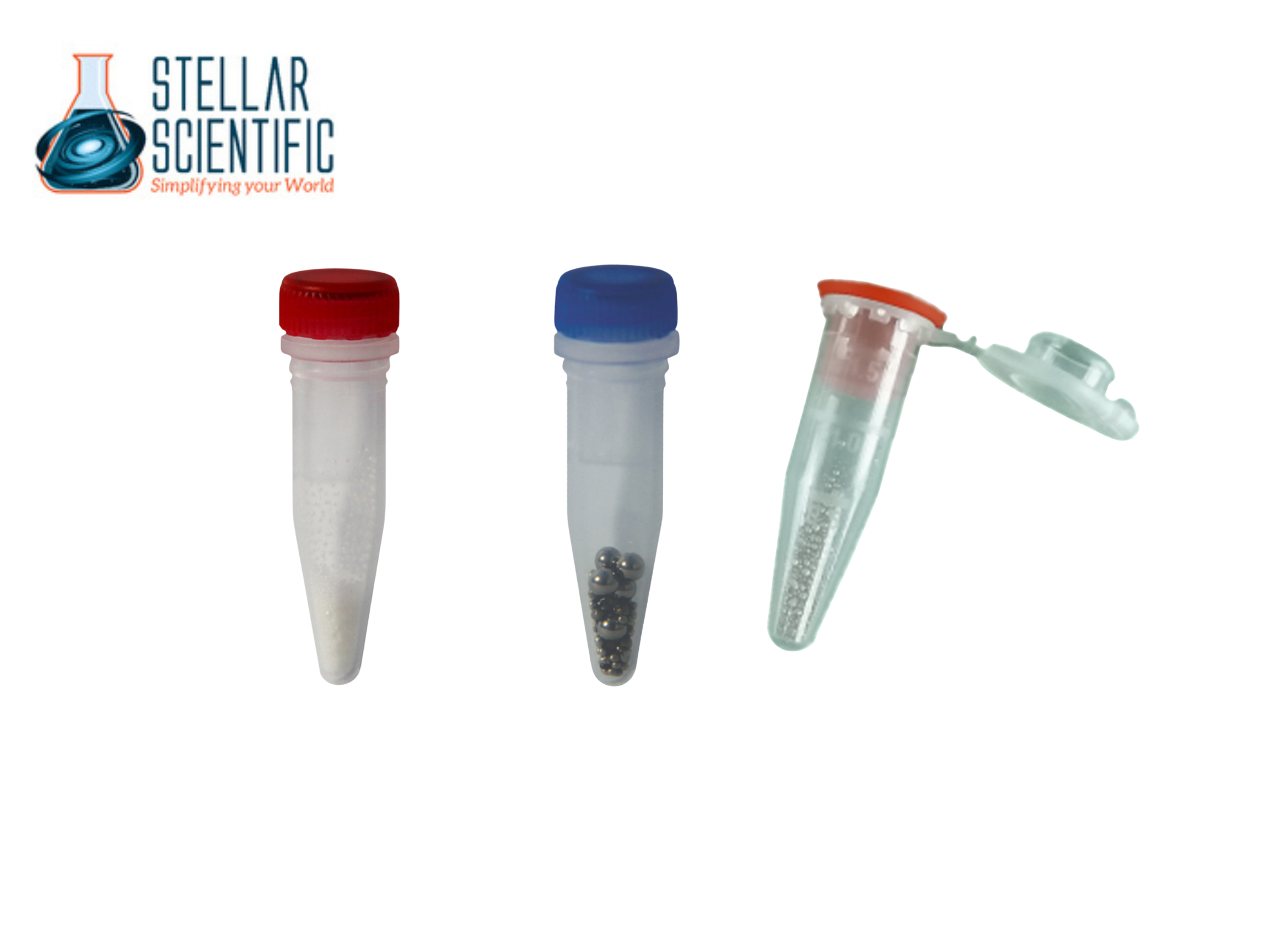
Homogenizer beads are small, spherical or cylindrical particles that come in a variety of materials, each tailored for different laboratory applications. When placed in a tube with your sample and agitated in a bead tissue homogenizer, these beads collide with the material, physically breaking down cell walls and releasing biomolecules for analysis.
Common Materials for Homogenizer Beads:
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for tough, fibrous tissues like animal samples and plant matter. Durable and highly effective for homogenizing hard-to-process samples.
- Ceramic: Gentle on more delicate materials, making them a great choice for RNA extraction and genomic studies.
- Glass: Non-reactive and perfect for biochemical applications where contamination must be avoided.
How Do Homogenizer Beads Help in Molecular Research?
The main function of bead homogenizer is to facilitate the homogenization of biological samples. This process involves rapidly agitating the beads and sample within a homogenizer, creating shear forces that break down cell walls, tissues, and other materials. As the beads collide with the sample, biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins are released, which can then be used for further analysis.
This is a key step in preparing materials for a variety of molecular research applications, including:
- DNA/RNA Extraction: Essential for isolating nucleic acids from tissues or cells.
- Protein Extraction: Critical for obtaining proteins from samples for subsequent analysis.
- Microbial Studies: Breaking down microbial cell walls for microbiological experiments.
How Do You Choose the Right Homogenizer Beads for Your Research?
Selecting the right homogenizer beads depends on several factors, including the type of sample you're working with and the analysis you intend to perform.
1. What Bead Material is Best for Your Samples?
- For Tough or Fibrous Samples: If you're working with difficult tissues, such as animal or plant matter, stainless steel beads are the most effective choice. These beads are durable and can handle high-speed homogenization.
- For Delicate Biomolecules: If you’re focused on preserving RNA or working with sensitive materials, ceramic beads are gentler and minimize sample degradation. Ceramic beads are commonly used in genomic studies.
- For Contamination-Free Extracts: For biochemical extractions, glass beads are the go-to option due to their non-reactive properties, which help prevent contamination.
2. What Bead Size Should You Use?
Bead size plays a huge role in the homogenization process. Here’s what to consider:
- Smaller Beads: Best for soft tissues or liquids, where gentle homogenization is needed. They’re perfect for nucleic acid extraction because they won’t damage delicate molecules like DNA and RNA.
- Larger Beads: Required for tougher, more fibrous materials (like plant tissues or bone). Larger beads create more impact force, making them ideal for breaking down hard samples.
How Do Homogenizer Beads Improve the Homogenization Process?
Homogenization with beads is a straightforward process, but its success depends on several key factors:
- Sample Preparation: The sample needs to be prepared properly, and you should use beads of the right size and material for the task.
- Optimization of Speed and Time: The speed and duration of the homogenization process should be tailored to the sample type. For example, tougher materials may require higher speeds or longer processing times.
- Achieving Desired Results: After homogenization, the sample should be fully disrupted, enabling the easy extraction of biomolecules.
What Is the Best Practice for Using Homogenizer Beads?
To ensure the most efficient homogenization, follow these best practices:
- Bead-to-Sample Ratio: Make sure you're using the appropriate number of beads. Too few will result in incomplete homogenization, while too many could cause excessive sample shearing.
- Speed and Time Settings: Adjust the homogenizer's speed and time based on the toughness of your sample. Higher speeds may be necessary for tougher tissues, while lower speeds could suffice for delicate samples.
- Trial Runs: Always perform a trial run to fine-tune bead size, material, and homogenization settings for your specific needs.
How Do You Clean and Maintain Homogenizer Beads?
Cleaning your tissue homogenizer beads after each use is essential to prevent contamination and ensure accurate results in future experiments. Here's a quick guide to cleaning different bead materials:
- Stainless Steel and Ceramic Beads: Clean with a mild detergent and warm water.
- Glass Beads: These require a more delicate cleaning process, so follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully to avoid damage.
How Can Homogenizer Beads Enhance Your Laboratory Research?
Homogenizer beads are an indispensable tool in molecular biology, allowing for faster and more efficient sample preparation. Whether you’re isolating DNA, extracting proteins, or preparing microbial samples, using the right homogenizer beads can make a significant difference in the quality and yield of your results.
For the best selection of homogenizer beads and accessories, visit Stellar Scientific. Our range of high-quality beads will enhance your research and help you achieve precise, reliable results every time.
Ready to Get Started?
If you need advice on choosing the right homogenizer beads for your research, contact us today. Visit Stellar Scientific's Product Page to explore our full range of laboratory equipment designed to streamline your sample preparation process.